ffuf
This section will cover ways to enumerate using ffuf.
Table of Contents
- Overview
- Basic Fuzzing
- Directory Fuzzing
- Extension Fuzzing
- Page Fuzzing
- Recursive Fuzzing
- Domain Fuzzing
- Sub Domain Fuzzing
- vhost Fuzzing
- Filtering Results
- Parameter Fuzzing
- Value Fuzzing
Overview
Fuzz Faster U Fool (ffuf) is a tool written in Go to perform fuzzing on websites.
Basic Fuzzing
This section will cover some basic fuzzing methods using ffuf.
Directory Fuzzing
To perform directory fuzzing, we can use the -u and -w options with ffuf. We can add the FUZZ keyword to specify the location to fuzz and :FUZZ to specify the which location to use.
ffuf -u https://<Target>/FUZZ -w /path/to/wordlist:FUZZ
Command breakdown:
-u https://<Target>/FUZZ- Specify the target URL to perform fuzzing.-w /path/to/wordlist:FUZZ- Specify the wordlist and fuzz location.
An example:
ffuf -u http://<Target IP>/FUZZ -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-small.txt:FUZZ
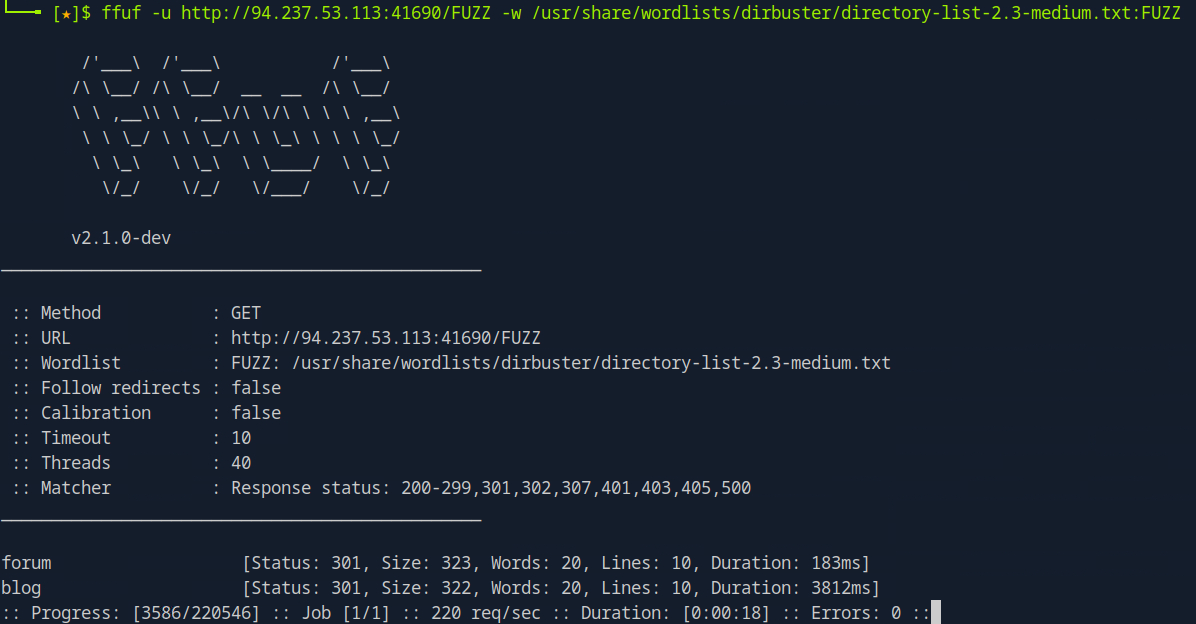
To increase the fuzzing speed, we can use the -t <value> option to specify the number of threads to use. It is not recommended to use large threads such as -t 200 as it may cause an Denial of Service (DoS) on the target.
Extension Fuzzing
We can fuzz for file extensions using the following.
ffuf -w /path/to/wordlist:FUZZ -u http://<Target>/path/to/indexFUZZ
An example:
ffuf -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/web-extensions.txt:FUZZ -u http://<Target IP>/blog/indexFUZZ
Alternatively, we can use the -e option followed by an extension to look for a specific extension.
ffuf -w /usr/share/wordlist/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt:FUZZ -u http://<Target IP>/blog/FUZZ -e .php
Page Fuzzing
We can fuzz for pages using the following.
ffuf -w /path/to/wordlist:FUZZ -u http://<Target>/path/to/FUZZ
An example:
ffuf -u http://<Target IP>/FUZZ.php -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-small.txt:FUZZ
Recursive Fuzzing
To perform a recursive scan, we can use the -recursion flag with the -recursion-depth flag. An example will be specifying the recursion depth to 1 which will for any sub directories in the found directory.
ffuf -u http://<Target>/FUZZ -w /path/to/wordlist/here -recursion -recursion-depth <value>
An example:
ffuf -u http://<Target IP>/FUZZ -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -recursion -recurison-depth 1
Domain Fuzzing
This section will cover some ways to fuzz domains.
Sub Domain Fuzzing
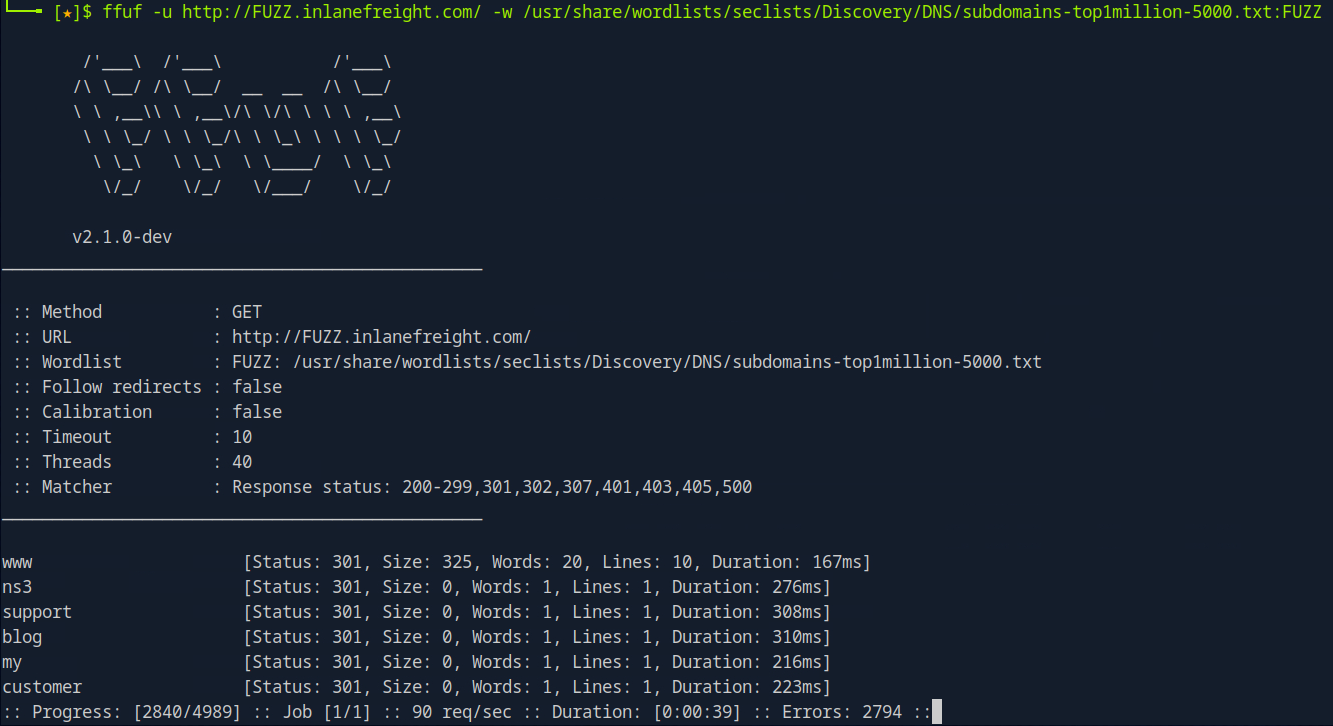
To perform sub domain fuzzing, we can use the following.
ffuf -u http://FUZZ.<domain>/ -w /path/to/wordlist:FUZZ
An example:
ffuf -u http://FUZZ.mycorp.lan/ -w main/wordlists/subdomains.txt
vhost Fuzzing
Virtual Hosts (vhosts) is a 'sub-domain' that is served on the same server and has the same IP address that is being used by two or more different websites.
vhosts may not necessarily have public DNS records.
To perform vhost fuzzing, we can use the -H flag to specify the header to use. We can use the Host header and specify the FUZZ keyword within it.
ffuf -u http://<Target>/ -w /path/to/wordlist:FUZZ -H 'Host: FUZZ.<domain>'
An example:
ffuf -u http://mycorp.lan/ -w main/wordlists/subdomains.txt -H 'Host: FUZZ.mycorp.lan'
Filtering Results
There are a lot of options that can be used to filter results. We can use the -h flag to view the available options. An example will be -fs which can be used to filter response size above the specified number.
ffuf -u http://<Target>/FUZZ -w /path/to/wordlist:FUZZ -fs <value>
An example:
ffuf -u http://mycorp.lan/FUZZ -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -fs 250
The above command will not display any request with the size above 250.
Parameter Fuzzing
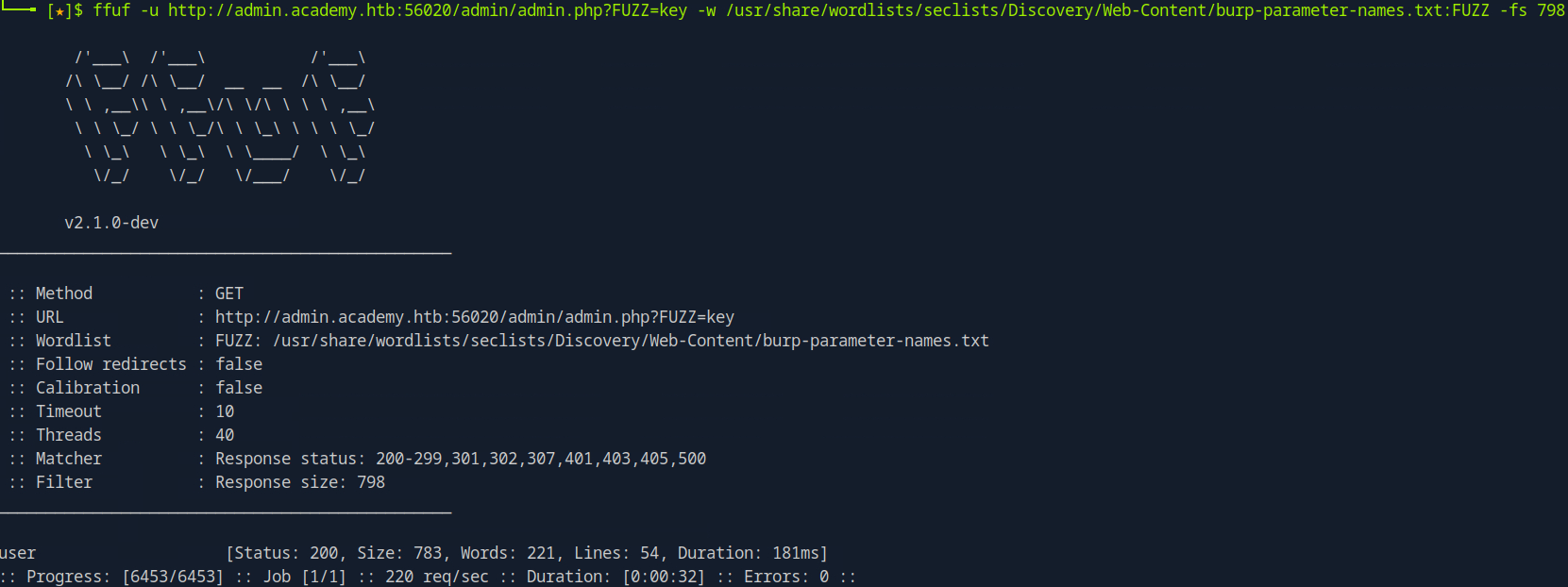
If the URL or site has a parameter using GET, we can fuzz it by replacing the existing parameter with ?FUZZ= in the URL.
ffuf -u http://<Target>/<page>?FUZZ=<value> -w /path/to/wordlist:FUZZ
An example:
ffuf -u http://mycorp.lan/admin?FUZZ=key -w main/wordlists/burp-parameter-names.txt:FUZZ
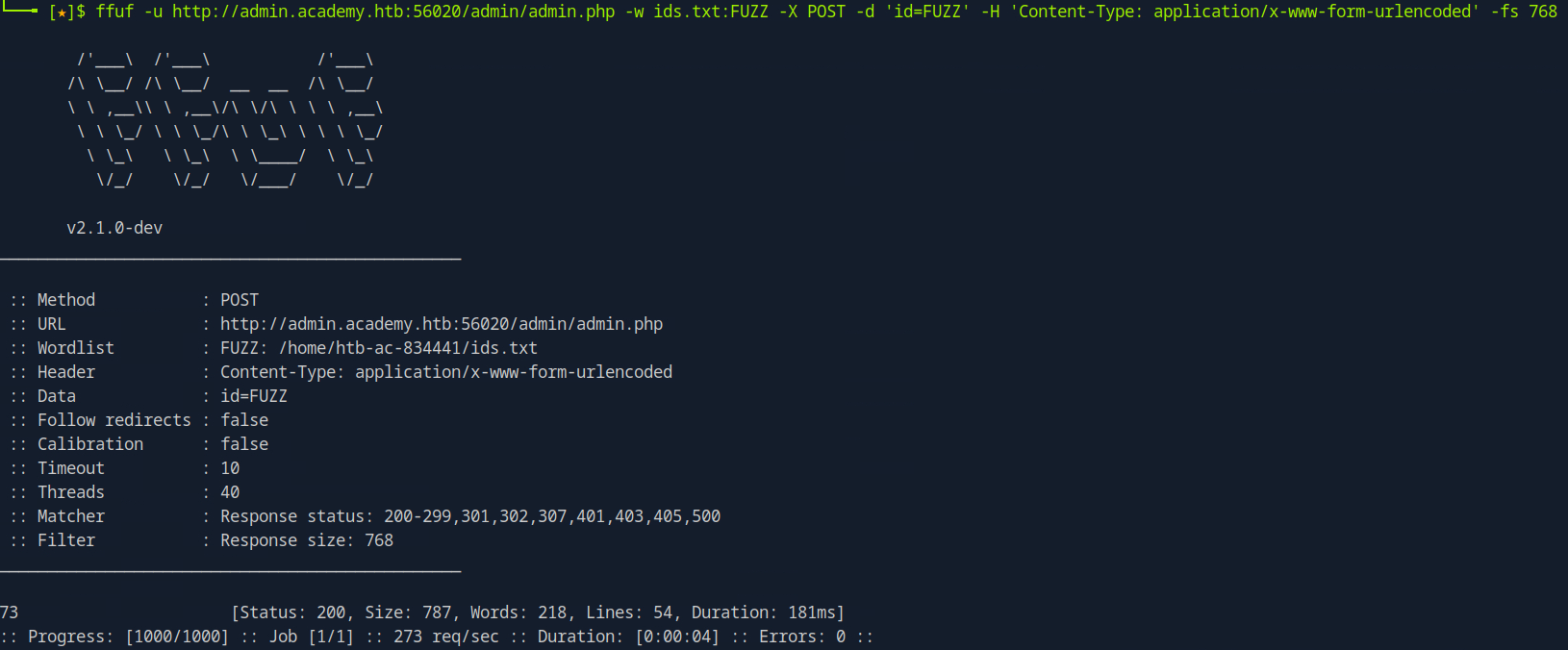
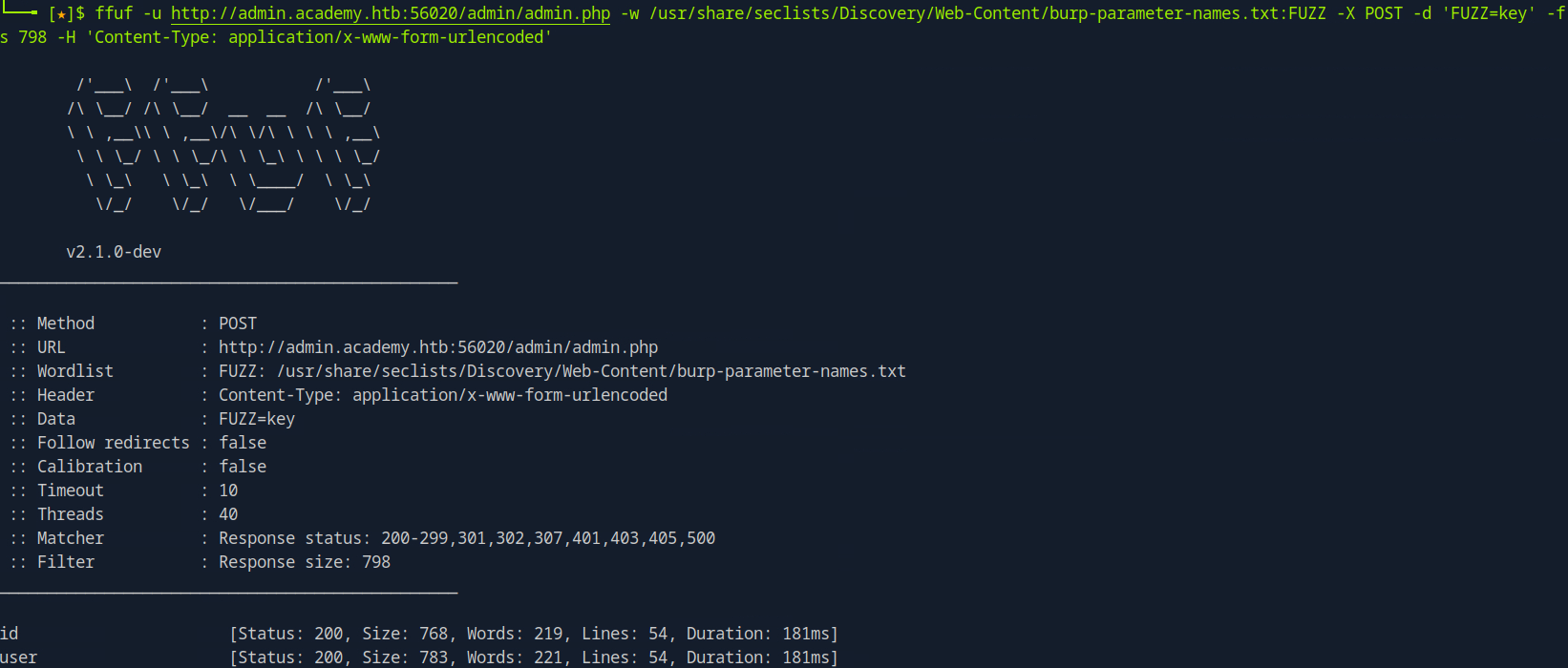
If the site is using POST, we can use -X and -d to specify the method and data respectively. This is because in POST requests, the parameters are not passed in the URL and cannot be appended with ?. Instead, data are passed in the data field within the HTTP request.
ffuf -u http://<Target>/ -w /path/to/wordlist -X POST -d 'FUZZ=<value>' -H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
An example:
ffuf -u http://mycorp.lan/ -w main/wordlists/burp-parameter-names.txt:FUZZ -X POST -d 'FUZZ=<value>' -H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
Value Fuzzing
Once we have found a valid parameter, we can fuzz the values for it by swapping the FUZZ position from the commands used in the parameter fuzzing section with the value.
ffuf -u http://<Target>/<page>?<parameter>=FUZZ -w /path/to/wordlist:FUZZ
An example:
ffuf -u http://mycorp.lan/admin?user=FUZZ -w main/wordlists/values.txt:FUZZ
Using POST:
ffuf -u http://mycorp.lan/ -w main/wordlists/values.txt:FUZZ -X POST -d 'user=FUZZ' -H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded'